Hardy Weinberg's Principle
Hardy Weinberg's Principle: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Genetic Drift, Speciation, Hardy-Weinberg Principle, Gene Pool, Founder Effect, Allopatric Speciation, Sympatric Speciation, Bottleneck Effect, Industrial Melanism, Parapatric Speciation and, Directional Selection
Important Questions on Hardy Weinberg's Principle
The theory of Natural selection that explains the appearance of new forms of life on earth was given by.
If the high altitude birds become rare or extinct, the plants which may disappear along with them are
A hypothetical plant species show two flower colour phenotypes - red and white. Red is dominant over white. In a population, this flower colour locus was found to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. If 490 out of a total population size 1000 plants were found to be white-flowered, how many of the red-flowered plants will be homozygous?
In a random mating population, frequency of recessive gene is 0.5. Then what is the frequency of dominant phenotypes in the population?
Frequency of an allele in an isolated population may change due to :
Can the Hardy-Weinberg principle be used to predict the frequency of the presence of the sickle cell allele in a sperm cell? Why or why not?
In a population of 1000 individuals, 25% of individuals show the phenotype for sickle cell anaemia (genotype - ss). Assuming the population meets Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, how many individuals would be carriers of the sickle cell allele but will not show the sickle cell phenotype?
Assertion: Adaptation enable the organisms to survive in stressful habitat.
Reason: Adaptations are not fixed genetically but take long evolutionary time to stabilize.
The correct option among the following is:
In a large, randomly mating population, only one person in 10,000 is an albino. What will be the frequency of a carrier person of albinism?
Phenylketonuria is an autosomal recessive disorder in man. If the frequency of affected newborn infants is about 1 in 14,000, assuming random mating, what is the frequency of heterozygotes?
A sample of sunfish population was studied for two parameters, i.e. body length and weight. The following graph was obtained.
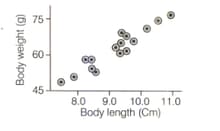
If the data is converted into a frequency polygon to study the distribution of body lengths, the pattern obtained would be:
Identify the type of natural selection in which more individuals acquire mean character value.
If the gene frequency occurs by chance it is termed as:
The pattern of natural selection that converts a unimodal distribution of a given phenotype into a bimodal is:
Define Founder effect. Give one example.
What are the types of natural selection
A bird species is restricted to Narcondam island () in Andaman and bird species is restricted to Middle Andaman Islands has an area of and has an area of . Based on the fossil record, a researcher found a common ancestor of species and in Myanmar, which had a long and pointed beak. Almost all members of the population of species have a long and pointed beak that is specialized to feed larvae of the beetle Wallace, found only on coconut trees in . Most population of species either have a very short and blunt beak to break open nuts or long and blunt beak to feed on small lizards. Very rarely members of species are found with long pointed beaks. Given this scenario, choose the correct statement from the following.
